36
PhotoRefractive Keratectomy
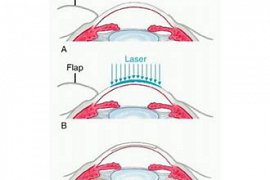
or PRK or LASEK, somehow, laser eye surgery is for the correction of refractive errors in people ... the camera and astigmatic used. In this action to shape the cornea and correct diagnostic, refractive, similar to LASIK of the excimer laser used; but, unlike Lasik, does not require the use of the device and remove the top layer of the cornea. but also for vision correction surface of the cornea (after scraping the cells of the surface or epithelium) directly, the laser can be. PRK on people when the cornea is thin, or disorder, the cornea, another specific. is more appropriate. Also PRK in people, army, etc. athletes, especially martial arts, and some other jobs more suitable. PRK in 1995 for the correction of myopia, and in 1998, to correct hyperopia approved by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) and was very low risk. Snuggly in the action layer (the flap) is removed is not complications related to the removal of the flap does not exist. In PRK, the removal of tissue from the center of the cornea. the slope of the curvature, it has less myopia can be corrected. To correct hyperopia, by removing the tissue from the part of the peripheral cornea., the slope of the curvature of the central, it is more and hyperopia can be corrected. To correct astigmatism, etc. of the cornea, so, given that the spherical shape turns.
part of the stages of laser surgery PRK is similar surgery LASIK. but the major difference is that in LASIK, after removing the layer of the cornea, with laser some tissue from the middle of the thickness of the cornea, shaved to be, but in the laser, PRK, laser energy on the surface of the cornea is applied.
prior to surgery. full medical examination and eye done. Refraction surveys accurate to determine the score, done. Map of Opotiki, a certain called "topographic" or "Tullahoma scan" is also to assess the situation, the optics of the cornea should be prepared. The thickness of the cornea is also a method called "pure metric" to be measured.
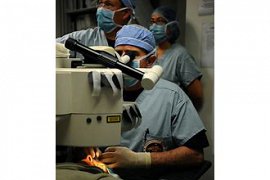
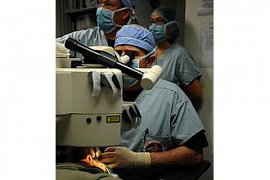
during surgery, with antiseptic (Betadine) of the eyelids and around the eyes and antiseptic. Drop, anesthesia, and antibiotics into the eye and poured the patient on the bed in front of the microscope long it takes.
by special to the name of the "speculum" gently in the eyes, can be laid up of the Open hold. so that you can't blink, but you can move your eyes. Eye with saline wash given. Layer of cells, the protective surface of the cornea is removed. Surgeon, you will have to light little red blinking inside the microscope, stare. If at all during the action, you are unable to visit the light stare, don't worry; The because most laser devices today equipped with radar, and may not move sadly, the eyes chase you. The surgeon with the use of the "excimer laser" myopia, far sightedness or astigmatism you make. Device excimer laser with the schedule calculated based on measurements before surgery. Tags light waves laser to distinct points of the cornea can shone, diagnostic, refractive eye you carefully corrected. Depending on the number eye, time laser per eye usually 1-2 minutes it takes. Then contact lens soft dressing, the cornea can be laid, until the restoration of the surface layer of the cornea be expedited. In the end, a speculum of the eye is removed and the technician operating room a Drops, antibiotics, other per eye you down.
a few hours after the procedure eyes pain and irritation will be. The next day the direction of the examination and the control to see the doctor. The first few days after surgery may feel a foreign body in the eye of the mind, which is normal. After a day of practice, your eyesight significant improvement will miniatu .. but to get to see the final few weeks time necessary. so, restoration of the operation site, and complete should wait a while. Early after surgery might eyes sensitive to light or not light the lights on the night of the broadcast, that this disposition gradually better. therefore, during the first few weeks after the operation, in an outdoor setting, from sunglasses to use.
in the United States of PRK for the treatment of from 1 - to 7 - verified. Nowadays, due to complications, PRK most eye doctors tendency of re to this practice have found; so that, in equal conditions surgery PRK prefer. In people who the thickness of cornea. individuals, athletes, and the army, PRK is more appropriate.
the benefits of surgery PRK:
for myopia, far sightedness, and astigmatism low to moderate is more appropriate.
during the practice time compared to LASIK shorter.
complications related to the creation of pants, such as: the incidence of inflammation, depth of the cornea (DLK), the wrinkles, the flap, separate full flap, etc. cutting an incomplete flap, and... does not exist.
to and technology relevant not need.
in the cornea, thin.
in the people, army and athletes, is more appropriate.
disadvantages of PRK:
pain and discomfort after the surgery, more and longer.
recovery time and duration time of need to the drug is longer.
in high numbers may cause opacity of the cornea....