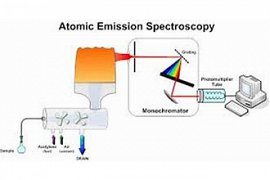
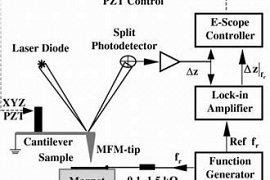
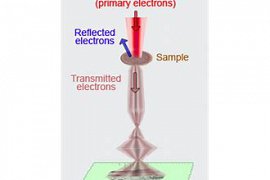
29
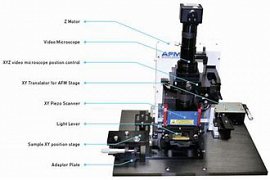
Super resolution Aperture Scanning Microscope
Microscope optical near field typical microscope probe is to check the structures of the NM goes to work.
study the materials and structures in the size of the micro-and nano need to the microscope, with the power breakdown of the top. that because of the limitation of diffraction governs the microscope, the classic, in which lenses are used. to achieve this breakdown with the use of this generation of microscope, is not possible. In order to achieve this goal, the microscope, the SEM images – survey were built, in that they review point to the object or the desired level and collect information, they analyze this data can be attributed to the morphology and the properties of the surface of the sample desired....
study the materials and structures in the size of the micro-and nano need to the microscope, with the power breakdown of the top. that because of the limitation of diffraction governs the microscope, the classic, in which lenses are used. to achieve this breakdown with the use of this generation of microscope, is not possible. In order to achieve this goal, the microscope, the SEM images – survey were built, in that they review point to the object or the desired level and collect information, they analyze this data can be attributed to the morphology and the properties of the surface of the sample desired....