11
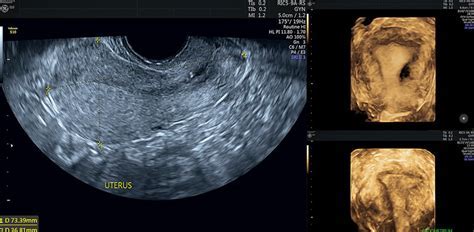
Trans Vaginal Sonogram
Transvaginal ultrasound iodine, is one type of ultrasound that is prescribed for women and expectant mothers. This vaginal ultrasound is very accurate in diagnosis and helps the doctor to better diagnose the disease or the patient\'s health. Transvaginal ultrasound using high-frequency sound waves, creates and shows images of the internal parts of the body. Although abdominal ultrasounds are accurate and show accurate information about the internal parts of the abdomen, they are not very accurate about the pelvic organs, and the best suggestion for examining the pelvic organs is to use a transvaginal. in transvaginal ultrasound unlike normal abdominal ultrasound where the transducer is placed on the abdomen, the respective doctor inserts an ultrasound probe, which is about 2 or 3 inches, into the vaginal canal. Doctors use this ultrasound to examine female reproductive organs such as the ovaries, erus, cervix, fallopian tubes and bladder. These organs are easily visible through the vagina.
use cases of trans-vaginal ultrasonography:
- hip pain
- bleeding, unusual vaginal
- examination, abnormal pelvis or abdomen
- a pregnancy outside the uterus
- check for cysts or fibroids uterine
- na fertility
- confirm placement IUD fit
- cancer of the reproductive organs...